We are glad to announce the "14th Annual Congress on Bioavailability and Bioequivalence (BABE 2023), scheduled during March 30-31, 2023 Dubai, UAE is currently a well-known event that draws participants from around the world who are interested in sharing, exchanging, and exploring new directions in neurology and neuroscience as well as recent advancements in related research. At this two-day international conference, academics and business veterans will be among the more than 30 plenary speakers at the highest level. It serves as a venue for discussing issues that arise during actual practises or research into neurological diseases in order to raise awareness and develop practical solutions.
You can take part in lively debates and cutting-edge lectures given by leading professors and scientists in all areas of bioavailability and bioequivalence. Leading academic scientists, researchers, and scholars will be gathered during BABE 2023 in order to exchange experiences and research.
Why to attend???
The conference will feature a variety of engaging academic programming, such as numerous discussions, workshops, lunches with affinity groups, paper presentations, and professional-led scientific sessions. However, each participant receives accreditation for their involvement, the development of their own brand, and the restoration of their consumer base. The delegates and highly qualified lecturers will have all necessary basic comforts, and attendance will have access to a source of information about all the next innovations planned.
Target Audience
The target audience will come from both the commercial and academic worlds, and will include
-
Pharmacist Allied Health Personnel
-
Bioinformatics
-
Neurochemistry
-
Pharmacologists in Clinical and Cellular Practice Neurologist
-
Biotechnology Experts
-
Neuropharmacology
-
Neurophysiologist
-
Neuropsychologist
-
Neuroradiology
-
Psychobiologist
-
Medical Psychologist
-
Pharmaceutical Formulations Used by Psychiatrists
-
Manufacturing
-
delivery of drugs
-
Bioavailability
-
Drug Evaluation
-
Delivery Equipment
When administered by an extravascular route, a drug's total bioavailability is typically less than one. There are a number of physiological variables that reduce the availability of medicines before they enter the systemic circulation. Whatever medication is taken with or without food will also affect absorption. Other medications taken at the same time may change absorption and first-pass metabolism, intestinal motility may change how the medication is terminated, and intestinal microflora may affect how much of the medication is chemically humiliated. There will also be a conclusion regarding conditions that impair the function of the digestive system or the liver.
-
Hepatic first-pass effect
-
Factors affecting bioavailability
-
Route of administration
-
Relative bioavailability
-
Absolute bioavailability
The VALUE Therefore, two medications with the same active component, such as a brand-name medication and its generic equivalent, or two distinct dosage forms of the same medication, such as an oral suspension and a tablet, have homogenous bioavailability and produce the same result at the site of physiological activity when administered at the same molar dose under the atmosphere. As a result, their results can be expected to be nearly identical.
-
In vitro Bioequivalence
-
Clinical trial formulations
-
Therapeutic index
-
Generic drugs
-
Bioequivalence of endogenous substances
Inherent heterogeneity has Excipients of many medications, including carbamazepine, show polymorphism. Different polymorphs dissolve differently. Using an amphiphilic mixture, dilute and dissolve Endogeneous,amphiphiles. They are lecithin, monooleins, and bile salts. Exogenous amphiphiles and Ionization Range
The relative bioavailability of the brand-name drug in comparison to the generic drug is used to compare bioequivalence for oral medications. For new drugs and drug effects, food effect bioavailability studies are frequently carried out during the investigational new drug (IND) phase to evaluate the effects of food on the rate and proportions of drug absorption when the drug product is managed shortly after a meal fed conditions, as opposed to commanding under diet conditions.
-
WHO Approaches
-
FDA Approach and regulations
-
TGA and risk management approach
-
Food-Effect Bioavailability and Fed Bioequivalence Studies
-
European Guidelines
In vivo/In vitro investigations: When comparing published human in vivo studies to in vitro drug release connecting imitation and drug intelligence into porcine skin ex vivo. Three retail econazole nitrate (EN) creams and two betamethasone valerate (BMV) formulations were estimated. Dermatopharmacokinetics. ransom test in vitro. Skin penetration in vitro Skin rash that is round, red, itchy, and scaly.
Any study's design is more important. After that, analyse the results because a poorly designed study cannot be fixed, but a poorly reviewed study can be revised to get valuable results. Instead, the design of the study is important for how well the data it produces can be examined. The study's scientific validity and the reliability of its data are essentially dependent on the study's design. Study designs are a collection of methods used to gather and analyse data for studies. Analytical studies and descriptive studies are the two main categories of study designs.
A biologic product is an entity created from living organisms, such as human, yeast, animals, or microorganisms, and acting as a therapeutic medicine or vaccination. Proteins and their constituent amino acids, sugars for carbohydrates, and nucleic acids for DNA make up biologics, which are flexible. Additionally, biologics may be tissues or cells used in transplants. The Biosimilars is a medicinal medicine that is structurally similar to a biologic brand but is rarely mentioned in relation to biologics.
-
Analytical techniques
-
Cancer therapies
-
Cardiovascular therapies
-
Diabetes therapies
-
Cancer therapies
-
Biosimilars: Regulatory Approach
The development of a pharmaceutical molecule in the pharmaceutical business requires bioequivalence studies. They base their argument on the observation of pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic parameters following the administration of tested medications. In pharmacokinetics, the term "bioequivalence" is used to evaluate the potential biological equivalency of two different drug formulations in vivo.
-
Novel Drug Delivery Systems- BA/BE approach
-
Generic drugs: Current claims and future directions
-
BA/BE Studies for Immediate-Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms
-
Bioequivalence analysis of highly variable drugs
-
Bioavailability Study for cancer drugs
-
Food-effect Bioavailability and fed Bioequivalence studies
Clinical trials are a subset of research that evaluates the effects of novel diagnostic procedures and drugs on human health outcomes. Clinical experiments involving volunteers are being conducted to examine medical interruption. Treatments and preventive care are carried out using medications, cells, and other biological products in addition to radiological, technological, and surgical methods. Clinical trials are meticulously planned, evaluated, and finished before they can begin. Children as well as adults of all ages may participate in clinical trials.
Clinical pharmacology lies at the nexus of advanced medication therapy for human disease and fundamental pharmacology. Clinical pharmacology has become essential for the development of surgery as well as for the proper understanding and use of modern medicine as a result of pharmacotherapy's dominance in therapeutics today.Pre-clinical research/trial
-
In Vitro and In Vivo investigations
-
Clinical Study Designs
-
Clinical Trial Management
-
Clinical Research Phase Studies
-
Bioequivalence Protocols: In vitro-In vivo Correlation
Animal models typically are unable to accurately reproduce an illness or disease. Increased clinical phenotyping and endotyping helps address issues related to the patient population's heterogeneity. Target identification and validation are improved as human data power is placed with more attention.
-
Topical Drug Development
-
Computer-Aided Drug Design
-
Rational Drug Design Approach
-
Novel Approach
-
Genetics in Drug Development
It is used to describe how pharmacological drugs are transformed by the body. so that it will be easier to end them. As the enzymes that speed up the reactions are diminished, a large number of metabolic processes that required medications take place in the liver. The liver is the main site of drug metabolism and must be crossed by the majority of medications. Once in the liver, enzymes change pre-medicated substances into active metabolites and change already-used substances into inactive ones.
-
Phase 1 metabolism of drug: P450 (CYP450)Enzyme
-
Phase I vs. Phase II Metabolism
-
Drug Efficacy and Toxicity
-
Drug Effects and Plasma Concentrations
-
Food/herbal remedies-drug interactions
A biosimilar is a biologic medicinal product that is very similar to another biological treatment that is already widely used. In the European Union, biosimilars must meet the same standards for pharmaceutical quality, safety, and efficacy as all biological medicines in order to be licenced.
-
Biosimilars in Therapeutics,
-
Biosimilars in Development, and
-
Biosimilars in Pipeline
They evaluated the antibiotic pharmacodynamics resource and reported the pharmacokinetics of specific antibiotic classes in critically ill patients. Aminoglycosides, beta-lactams, carbapenems, colitis, glycopeptides, tigecycline, fluoroquinolones, lincosamides, and linezolid are among the antibiotics and antibiotic groups judged.
-
Posology & Development
-
Pharmacokinetics
-
Pharmacodynamics
-
Drug Interactions
-
Drug Safety and Efficacy;
-
Drug Interactions
The term typically operates in a manner that incorporates many dose forms. The pharmaceutical medication output, as it is advertised for use with an unrelated combination of active ingredient and inert components, is the dosage conformation. It includes a capsule shell testimony for a certain dose. In a multistep process known as a pharmaceutical statement, the active ingredient is combined with all other ingredients while taking into account aspects like as polymorphism, particle size, pH, and solubility to create the final, effective medical product.
-
Immediate-Release Products
-
Topical Dosage Forms
-
Parenteral Dosage Forms
-
Solid Dosage Forms
-
Products with Modified Releases
Clinical trials are research projects conducted on individuals with the goal of estimating a medicinal, surgical, and behavioural intervention. Clinical trials are research projects carried out on individuals with the goal of evaluating a therapeutic, surgical, or behavioural intervention. Clinical trials are extensive human testing investigations intended to gauge the effectiveness of a medicinal, surgical, and behavioural intervention.
-
In Vitro and In Vivo investigations,
-
Clinical Study Designs,
-
Clinical Trial Management,
-
Clinical Research Phase Studies,
-
Re-Clinical Research/Trial,
-
Bioequivalence Protocols: In Vitro-In Vivo Correlation
Based on the medicinal material's solubility and absorptive properties, it serves as a compartment substructure. It is a tool used in the development of pharmaceuticals to describe "bio waiver" concurrently with the medication product's dissolution. Bio waivers based on the BCS When the dossier is accepted based on evidence of equivalence other than an in vivo bioequivalence test, it is necessary to request a bio waiver from the regulatory drug approval process.BCS bio waivers
-
Dissolution testing in drug formulation
-
In vitro preclinical ADME/BCS testing
-
In vitro drug product research
-
Preclinical and clinical testing for oral medication delivery
Biosimilars are medications that claim to have no clinical variability in purity, potency, and safety. These medications have a significant effect on people with a wide range of crippling and life-threatening illnesses, including rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, leukaemia, lymphomas, cardiac myopathies, and various oncogenic cancers.
-
Analytical techniques
-
Cancer therapies
-
Cardiovascular therapies
-
Diabetes therapies
-
Cancer therapies
-
Biosimilars: Regulatory Approach
Scope of Pharmacovigilance Drug Safety is extremely unbiased. a professional path that likely involves working in both permanent and temporary positions. Depending on the level of exposure attained, a career in drug safety may lean towards line management or a more technical path involving risk management, signal detection, and epidemiology.
The global biosimilars market ought to $60.1 billion by 2025 from $15.7 billion in 2020 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 30.9% for the forecast period of 2020 to 2025.
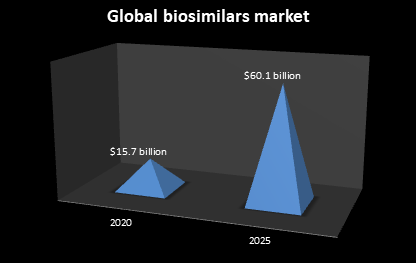
Report Scope
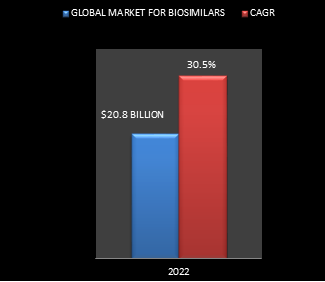
Biosimilar medication have gained huge quality because of their impact on the lives of many patients. These drugs belong to many drug categories that include hormones, interferons, growth factors (colony stimulating factors, erythropoietin) and monoclonal antibodies, among others. The use of these drugs has aided in the affordable treatment of many life-threatening diseases starting from cancer and diabetes to chronic inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis etc. The high cost of branded biologics has created biosimilars a lucrative alternative for affordable treatment. In line with the BCC Research report on biosimilars (BIO090C), the global market for biosimilars is expected to achieve on the point of $20.8 billion by 2022, growing at a CAGR of 30.5%. Alternative drivers for this market embrace rising aging populations, patent expirations of many blockbuster drugs, and better healthcare provisions.
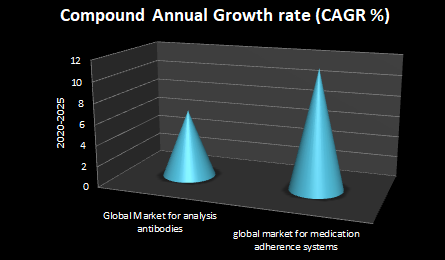
The global market for analysis antibodies ought to grow from $2.7 billion in 2020 to $3.7 billion by 2025 with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% for the period of 2020-2025.
The global market for medication adherence systems and technologies should raise from $3.5 billion in 2020 to $6.0 billion by 2025 with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.4% for the period of 2020-2025.
Medication adherence systems involve hardware-based systems (e.g., smart pill bottles, smart caps, automated pill dispensers, electronic trays, smart medical watches, smart medical alarms, wearable sensors and other packaging systems) and software-based internet applications (e.g., cloud-based databases, health programs, patient web portals, mobile medication management applications, etc.) designed to enhance medication adherence related with several chronic diseases. This report is an analytical tool whose primary purpose is to provide a thorough evaluation of the global market for medication adherence.




